Using Mingo to Analyze and Visualize FerretDB Data
No matter what type of database you have, you need the right tools to manage, query, and visualize the data effectively – and FerretDB is no exception.
As the truly open-source MongoDB alternative, FerretDB doesn't just let you use the same commands and queries as MongoDB, but it also enables you to take advantage of popular MongoDB tools and applications.
In the past couple of weeks, we've been testing FerretDB with many MongoDB GUI applications and written blog posts on them.
See the blog posts here:
In this blog post, we'll be exploring FerretDB usage with Mingo – a modern, sleek, and fast MongoDB GUI tool. With Mingo, FerretDB users can easily query, visualize, and analyze their database using Mingo's many interesting UI features.
Prerequisites
- Download and install Mingo from here
- Dockerto set up FerretDB docker installation (see documentation)
- mongosh
Installation and setup
FerretDB
To set up FerretDB, we'll be using the Docker installation. Set up the docker-compose YAML file with the following configurations:
services:
postgres:
image: postgres
environment:
- POSTGRES_USER=username
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=password
- POSTGRES_DB=ferretdb
volumes:
- ./data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
ferretdb:
image: ghcr.io/ferretdb/ferretdb
restart: on-failure
ports:
- 27017:27017
environment:
- FERRETDB_POSTGRESQL_URL=postgres://postgres:5432/ferretdb
networks:
default:
name: ferretdb
Ensure to update the authentication credentials username and password to match your definitions.
From the terminal, run docker compose up -d to start the services.
Mingo
Ensure that you have Mingo installed. If you don't, start by downloading Mingo from the download page. Then select the right software package for your OS.
Once the package is downloaded, install Mingo.
Now that we have installed Mingo, let's go into how you can connect Mingo to your FerretDB instance.
Connecting Mingo with FerretDB
Mingo is a MongoDB GUI, so you just need to provide the connection string for your instance, and it'll connect directly to FerretDB.
On the navigation bar, click "Connections" > "Manage Connections". Once you're in the Connections window, Click "Add connection" and enter the connection credentials.
To connect to FerretDB, we need to specify the connection URI string: mongodb://username:password@127.0.0.1:27017/?authMechanism=PLAIN.
Ensure to update the authentication credentials for username and password.
Test the connection and if it's successful, save it.
Add demo data
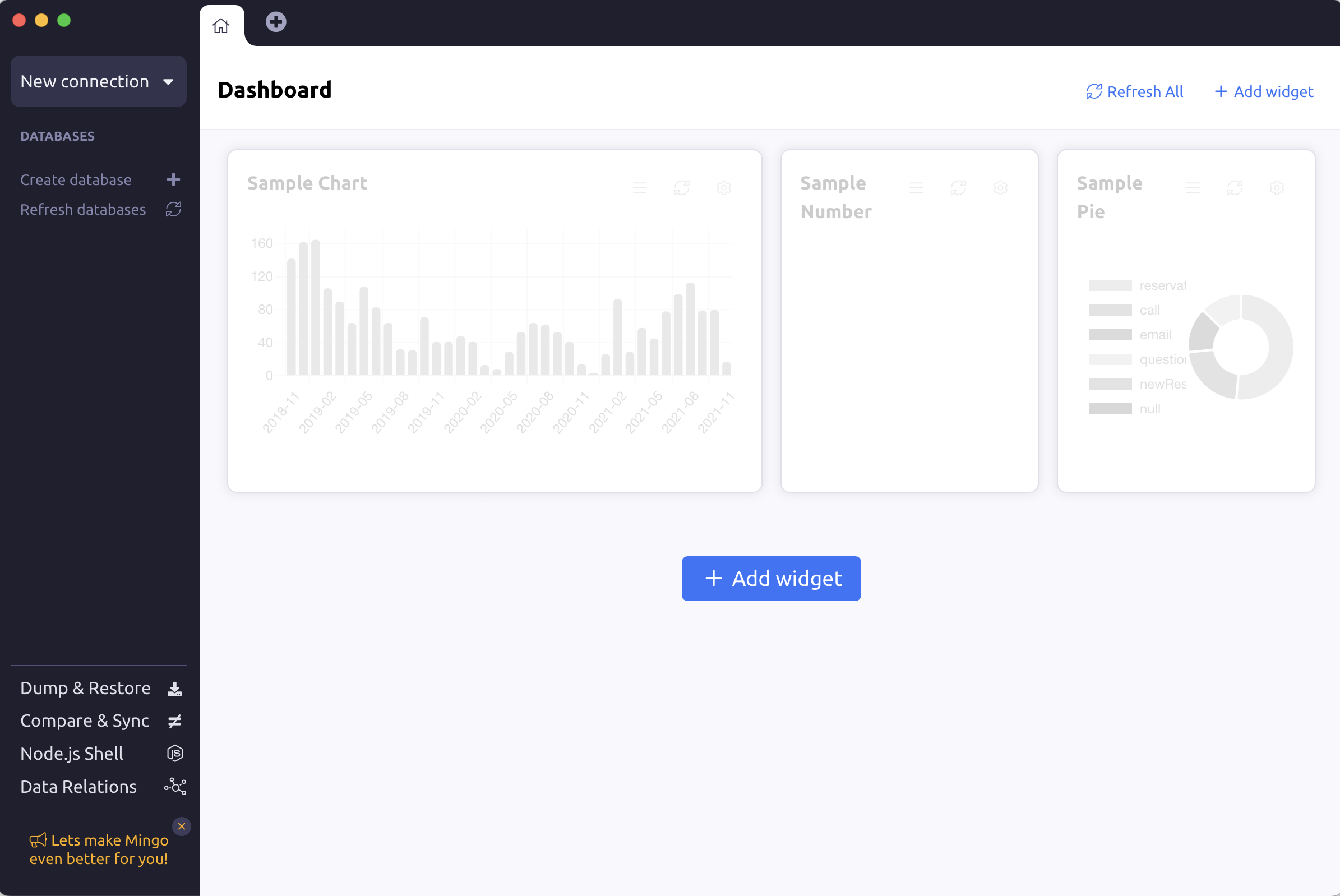
By now, you should see all your FerretDB databases on the Mingo dashboard, if there are any. If they are not visible, please click "Refresh databases".
For the purpose of this article, we're going to add some demo data for visualization in Mingo.
We'll be doing this through mongosh.
Please find the data here:
The data contains a set of documents based on different transactions and supplies across the globe. This is a sample document from the collection:
{"transaction_id": 10020, "customer_name": "María Pérez", "customer_location": "Buenos Aires, Argentina", "product_category": "Furniture", "transaction_time": new Date ("2023-07-16T02:00:00Z"), "product_name": "La-Z-Boy Recliner", "price": 450, "quantity": 1, "payment_method": "Credit Card"}
Analyzing FerretDB database in Mingo
Let's start by running some basic queries in the Mingo dashboard.
Refresh the database to see the data we just inserted and click on the collection to display all the data on the dashboard.
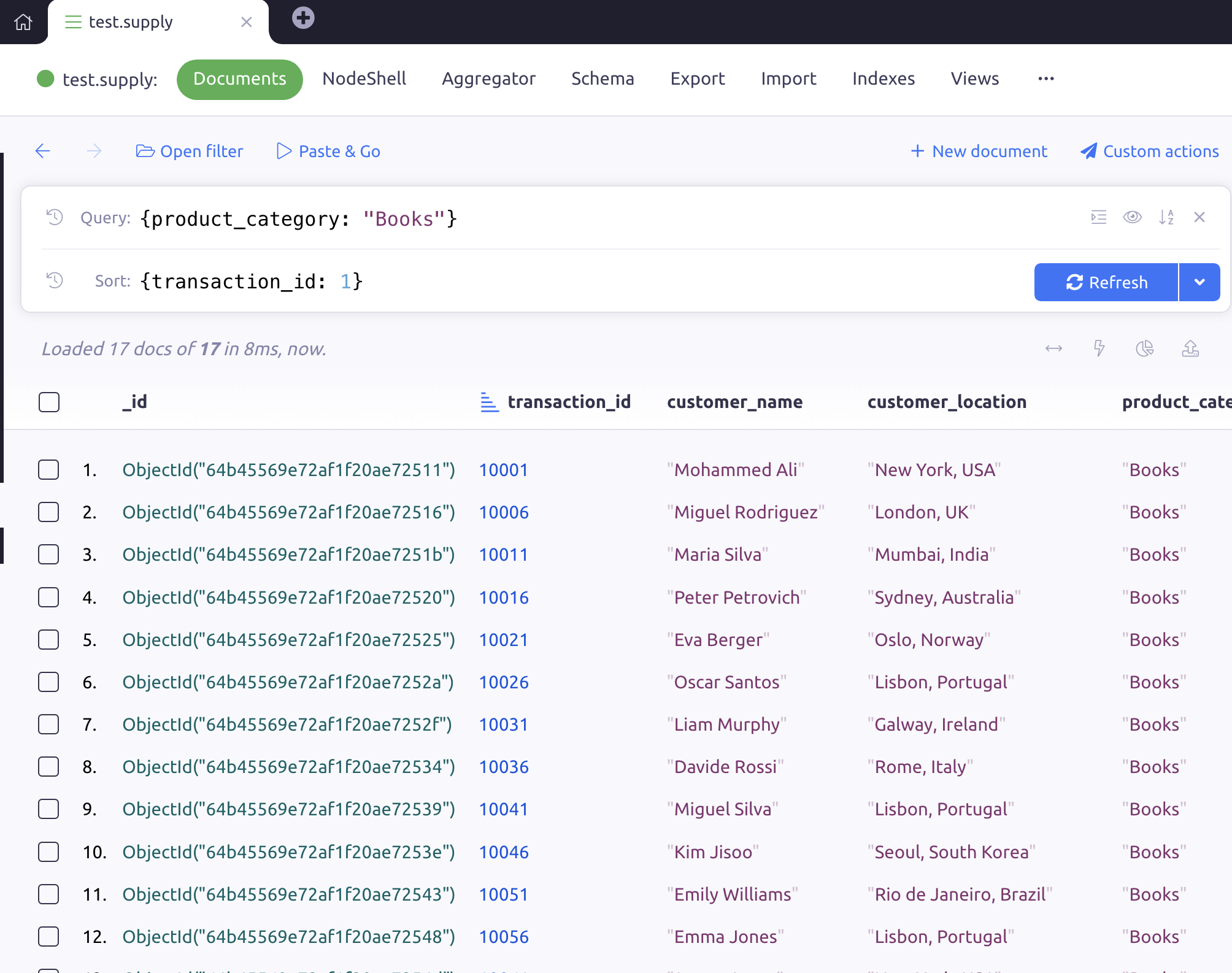
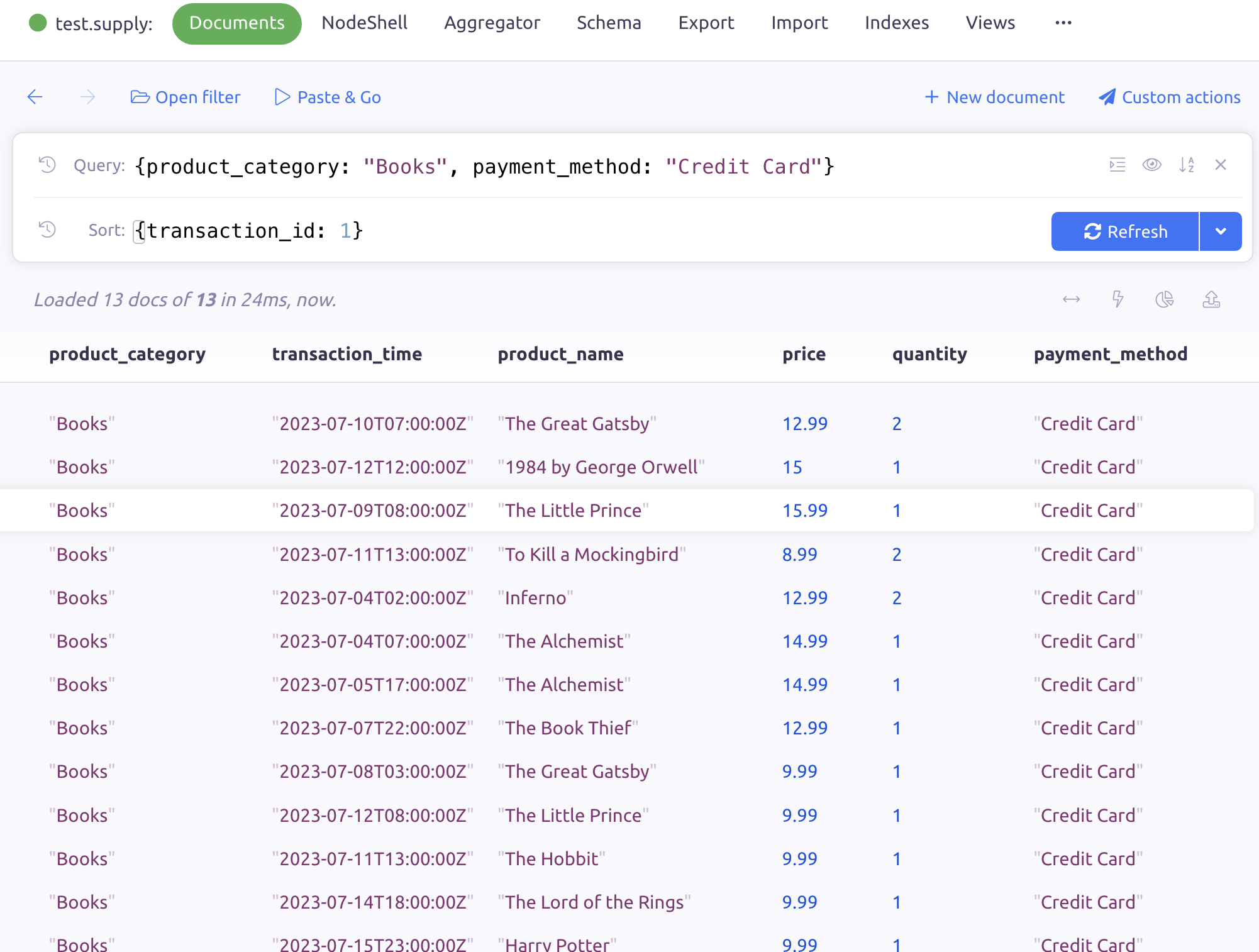
Scenario 1: Suppose you want to query the database for all transactions with the products category "Books" and payment method as "Credit Card" and sort based on the transaction_id.
You can do this through the query/sort section of the GUI.
The query expression will take this format {product_category: "Books", payment_method: "Credit Card"}.
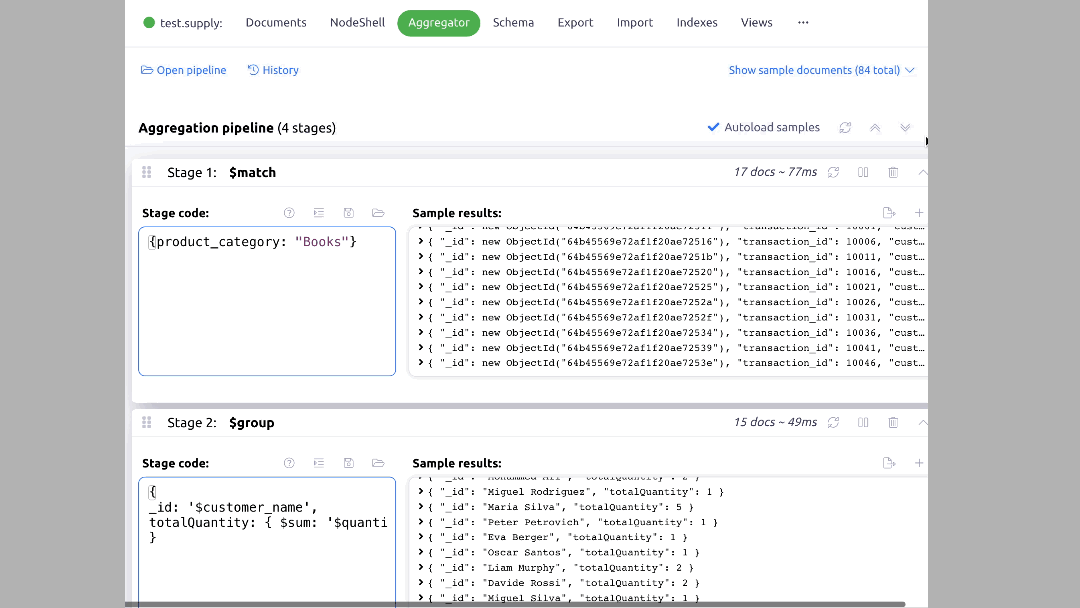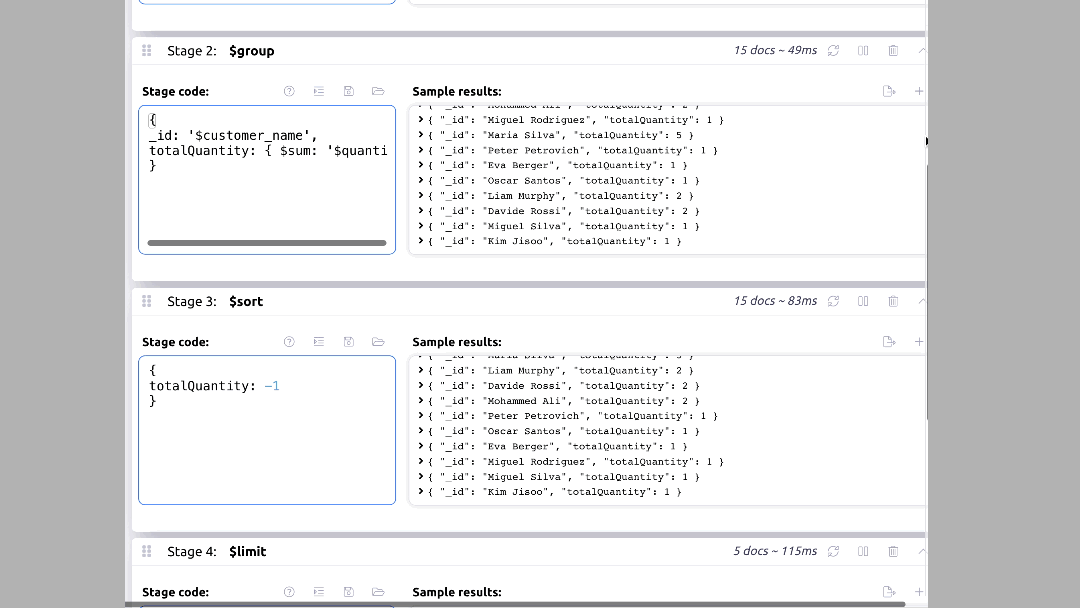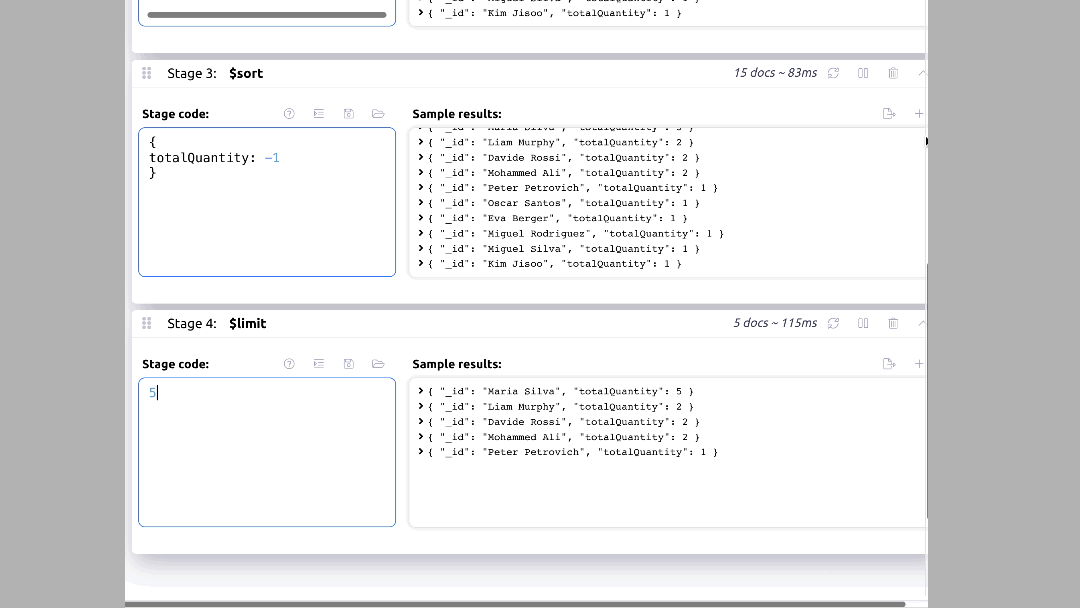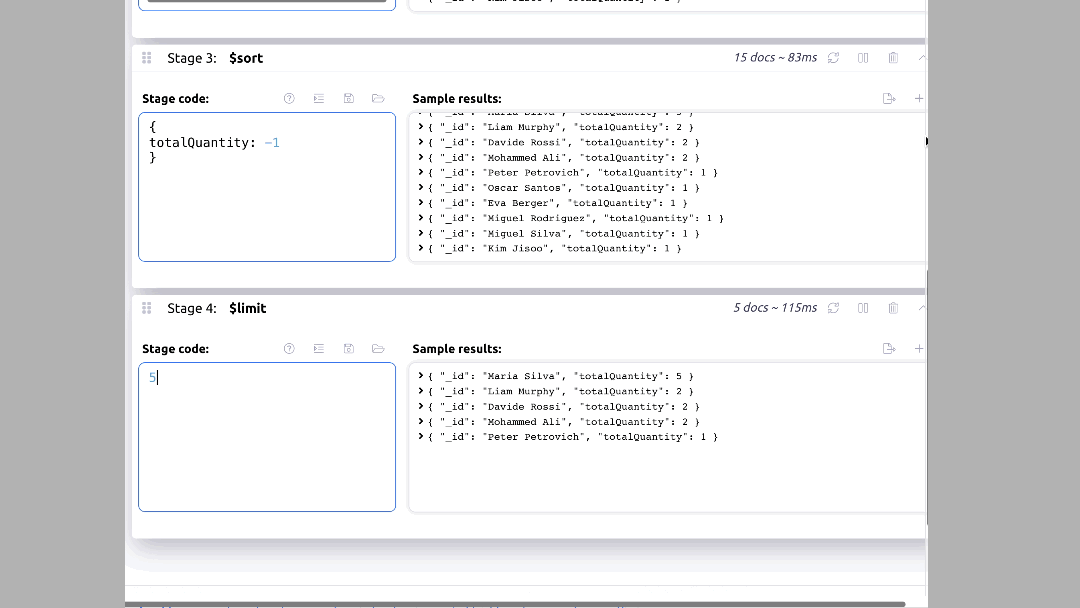
Scenario 2: Suppose you want to select the top 5 customers by the total quantity of books purchased.
You can do this through aggregation operations and use Mingo's user-friendly interface to set it up. A typical syntax for this would look like this:
db.supply.aggregate([
{ $match: { product_category: 'Books' } },
{ $group: { _id: '$customer_name', totalQuantity: { $sum: '$quantity' } } },
{ $sort: { totalQuantity: -1 } },
{ $limit: 5 }
])
In Mingo, you can set this up by clicking on the "Aggregation" tab and setting up the pipeline as shown below:
Scenario 3: In Mingo, you can easily query by time range and visualize the data on a chart.
There are different options avaialble including #last2weeks, #today, #lastWeek, among others.
Get started with FerretDB and Mingo
As we've seen so far, FerretDB is able to work seamlessly with Mingo, which is truly brilliant! This means FerretDB users can analyze and visualize their data right from the MongoDB GUI tool, leveraging user-friendly UI and intuitive features of Mingo.
This is yet another addition to the growing list of FerretDB-compatible applications, which ensures our community of users can leverage a truly open-source database that works seamlessly with their best tools; they don't have to worry about the vendor lock-in or license changes that is prevalent with proprietary databases like MongoDB.
If you're just finding out about FerretDB, and would like to experiment with it, please check out installation guidelines on how to get started.
And if you would love to leave a message or have any questions for our engineering team, we'd be happy to answer them. Please reach out to us on any of our community channels.